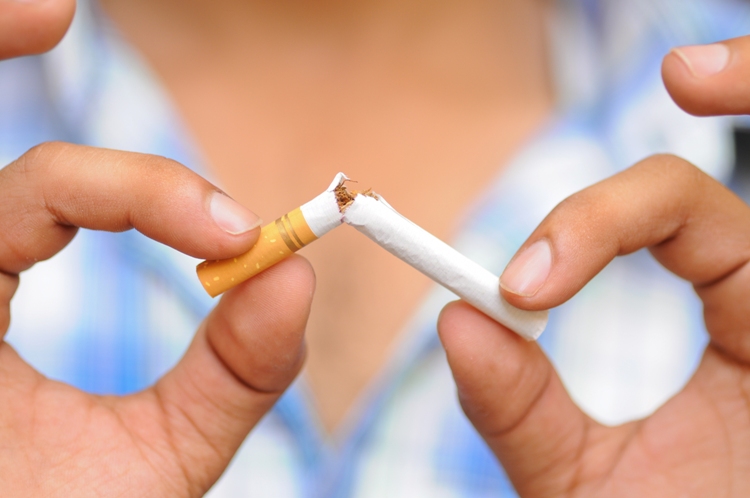
Smoking is responsible for several diseases, such as cancer, long-term (chronic) respiratory diseases, and heart disease, as well as premature death. Over 440,000 people in the USA and 100,000 in the UK die because of smoking each year. According the US CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention), $92 billion are lost each year from lost productivity resulting from smoking-related deaths.
Of the more than 2.4 million deaths in the USA annually, over 440,000 are caused by smoking.
Smoking is the largest cause of preventable death in the world. Recent studies have found that smokers can undermine the health of non-smokers in some environments.
In an article published online in Medical News Today on 30 May 2013, we presented data demonstrating that, on average, smokers die ten years sooner than non-smokers.
Smoking Causes Cancer
90% of lung cancer patients developed their disease because of smoking. Lung cancer is one of the most common causes of cancer deaths in the world. Smokers also have a significantly higher risk of developing:
- Bladder cancer
- Kidney cancer
- Cancers of the pharynx and larynx (throat cancer)
- Mouth cancer
- Esophagus cancer
- Cancer of the pancreas
- Stomach cancer
- Some types of leukemia
- Cancer of the nose and sinuses
- Cervical cancer
- Bowel cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- In some cases, also breast cancer
According to Cancer Research UK, one person dies every 15 minutes in Great Britain from lung cancer. Smoking also raises the risk of cancer recurrences (the cancer coming back).
Why Does Smoking Raise Cancer Risk?
Scientists say there are over 4,000 compounds in cigarette smoke. A sizeable number of them are toxic – they are bad for us and damage our cells. Some of them cause cancer – they are carcinogenic.
Related posts:
 Why it is Important to Eat Fruits?
Why it is Important to Eat Fruits?
 Nutritions for Kids: Guidelines for A Healthy Diet
Nutritions for Kids: Guidelines for A Healthy Diet
 Top Reasons to Exercise in the Morning
Top Reasons to Exercise in the Morning
 Benefits of Trees
Benefits of Trees
 Types of Tea and Their Health Benefits
Types of Tea and Their Health Benefits
 5 Breakfast Tips for Weight Loss
5 Breakfast Tips for Weight Loss
 10 Reasons Junk Food is Bad for Your Health
10 Reasons Junk Food is Bad for Your Health
 Tips To Prevent Spring Allergies
Tips To Prevent Spring Allergies
 ورزش کیلئے چند اہم ہدایات
ورزش کیلئے چند اہم ہدایات
 5 Best Foods for Building Muscles
5 Best Foods for Building Muscles
 10 Benefits of Fasting That Will Surprise You
10 Benefits of Fasting That Will Surprise You
 Guide to Healthy Fasting During Ramadan
Guide to Healthy Fasting During Ramadan




